AI on Mallampati Scoring and Endoscopy
Interpretability for Automated Mallampati Scoring and Endoscopy
“Multimodal Deep Learnings and Interpretability for Automated Mallampati Scoring and Endoscopy Prediction”
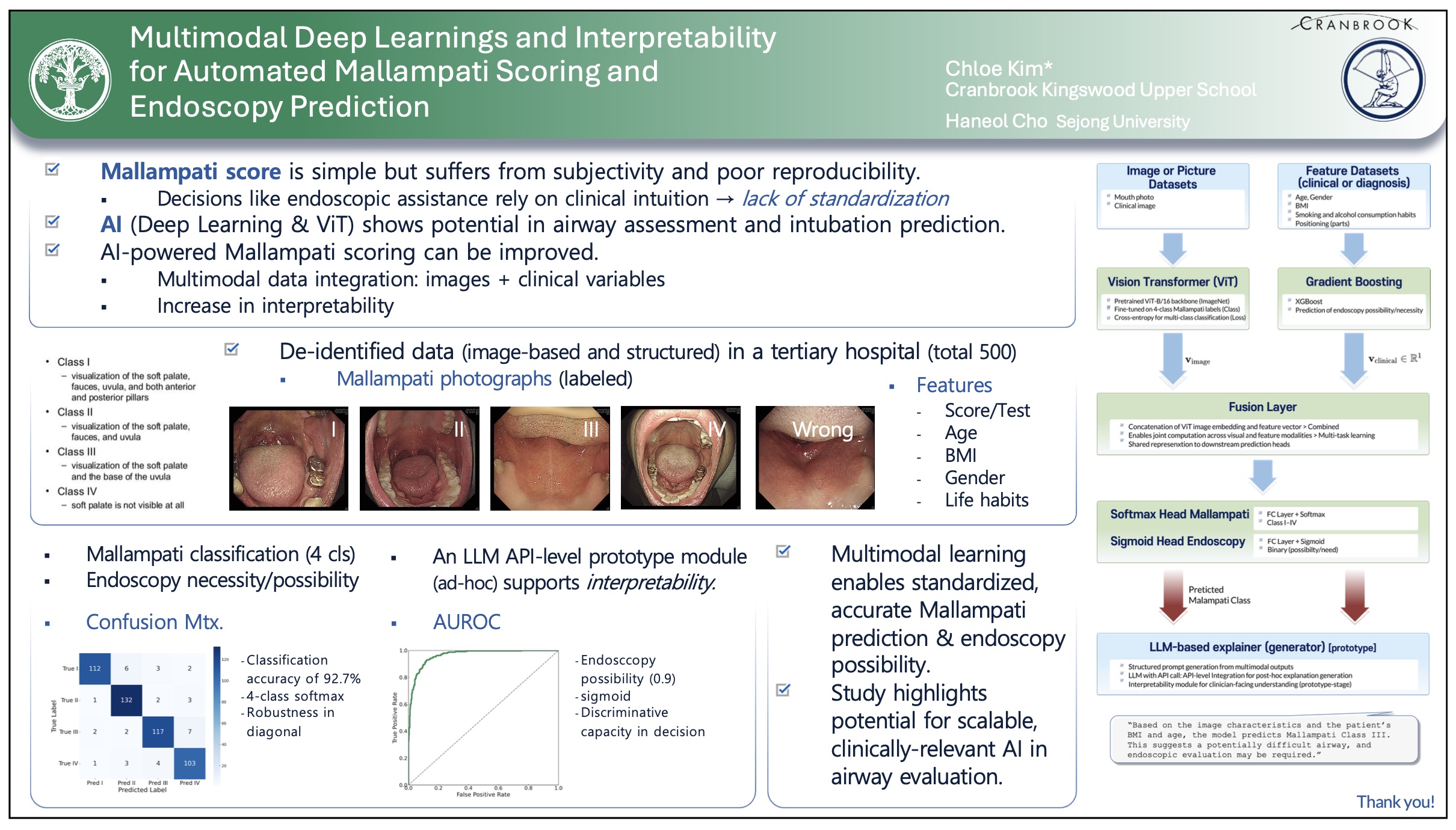
The Mallampati score is widely used to assess the difficulty of intubation and endoscopic procedures but suffers from high inter-rater variability. We present an AI model that automatically classifies Mallampati scores and predicts the need for endoscopic assistance using multimodal data. A dataset of 500 patients from a hospital in Korea was used, which includes Mallampati photographs and clinical variables. A Vision Transformer (ViT) processes imaging data, and gradient boosting is applied to clinical features.
These AI models are fused to predict Mallampati classes (I–IV) and the binary outcome of endoscopy necessity. Additionally, we integrate a large language model (LLM) to generate clinically interpretable explanations to support decision-making.
Our model achieves an accuracy of approximately 92.7% in Mallampati classification and an AUROC of 0.95 for endoscopy necessity prediction. This highlights the potential of deep learning interpretability to standardize airway assessments and support procedural planning.